- 00000018WIA30401970GYZ
- id_400264681.4
- Jul 20, 2022 4:16:54 PM
Star
Star may not be for sale in all markets due to approval or clearance by in-country regulatory agencies.
DISCO Star
Use DISCO Star for free breathing multi-phase acquisitions.
DISCO Star provides a better patient experience when it comes to abdominal MR imaging. Patients with limited breath-hold capability or patients unable to follow breathing commands now have the option of free-breathing dynamic abdominal imaging. With simple, push button dynamic imaging, technologists can overcome timing challenges for dynamic imaging and avoid repeat scans due to motion artifacts.
DISCO Star is a motion robust 3D radial (stack-of-stars) scan acquired in one continuous dynamic arterial phase to drive worry-free, consistent image quality regardless of the patient’s condition. DISCO Star employs radial in-plane trajectory to provide active motion compensation without navigators or respiratory gating.
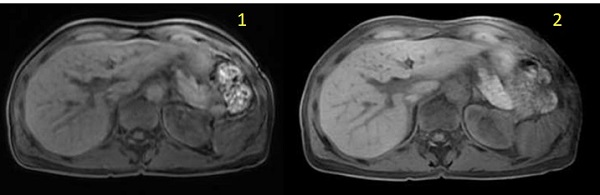
| Number | Description |
|---|---|
| 1 | DISCO free-breathing image |
| 2 | DISCO with Star Imaging Option free-breathing image |
LAVA Star
Use LAVA Star for free-breathing single-phase acquisitions.
LAVA Star provides the same motion robust, free-breathing scan for single phase (pre-contrast or delayed) imaging. Similar to DISCO Star, LAVA Star also employs radial in-plane trajectory to provide active motion compensation without navigators or respiratory gating.
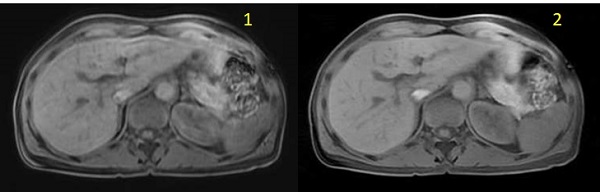
| Number | Description |
|---|---|
| 1 | LAVA free-breathing image |
| 2 | LAVA with Star Imaging Option free-breathing image |
Details
Stack-of-Stars is a 3D gradient echo imaging sequence that uses stacks of radial spokes to provide motion robust imaging. Readout and phase directions in conventional 3D Cartesian imaging are swapped with radial spokes in Stack-of-Stars trajectory. However, standard phase encoding gradients are used to sample along the slice direction. Stack-of-Stars trajectory is shown in the LAVA Star abomen images.
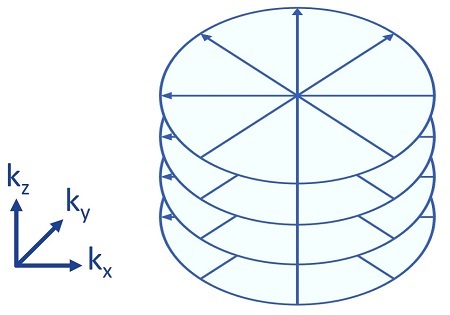
K-space data acquired with Stack-of-Stars trajectory are reconstructed with a technique which incorporates trajectory correction, sampling density correction, parallel imaging (if prescribed), view-sharing (if multiphase scan is prescribed) and active motion compensation. Active motion compensation module senses the respiratory motion and compensates for it to make sharper images for Star applications.
Considerations
- For more details about the multi-phase tab with DISCO Star, see DISCO Star.
- Star Imaging Option only appears if you have some combination of these Imaging Options: ARC, Spectral Spatial RF, ZIP1024, ZIP512.
- Increase the frequency value and the TE value increases, the spatial resolution increases, the SNR decreases, and the number of slices may decrease.
- The number of spokes is calculated internally based on the prescribed frequency, NEX and Phase Acceleration.
- Increase the NEX value and the number of spokes increases, SNR increases, scan time increases.
- Increase Phase Acceleration and the number of spokes decreases, SNR decreases, scan time decreases, and streak artifacts increase.
- Number of spokes is displayed in the series text page and in the DICOM header.
- Spokes on the series text page identifies the number of spokes acquired for reconstructing an image in the first phase when Series Per Phase is not selected.
- Number of Spokes field in the DICOM header identifies the number of spokes acquired for reconstructing the selected image.
- Streak artifacts might be seen in the images, especially in abdomen imaging, due to respiratory motion and arms motion. Consider increasing NEX and/or scanning the patient in arms-up position to mitigate the artifacts.
- Physiological motion, such as peristalsis and respiratory, might cause blurring in the images.
- Chemical shift effects appear as blurring in the images. Consider using fat suppression and/or high bandwidth to minimize the effects.
