- Object ID: 00000018WIA308F1970GYZ
- Topic ID: id_40023596 Version: 1.4
- Date: Aug 18, 2022 1:38:35 PM
Flex: display images
About this task
Step-by-step instructions
- From the Patient List, select the series with the Flex images.
- See Series numbering for series annotation details.
- Select the desired series and from the Session application list, click Viewer.
- The annotated NEX is different from the NEX value entered for the scan prescription. The annotated NEX reflects the value needed to optimize image quality and it is typically two times the NEX value entered (or three times for single-TR mode in 2D FSE and 3D Cube scans).
Figure 1. Flex NEX annotation and FLx Imaging Options annotation 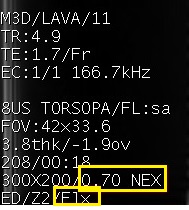
- Fat/Water/In-Phase/Out-of-Phase images are annotated in the upper left corner.
Figure 2. Flex image annotation 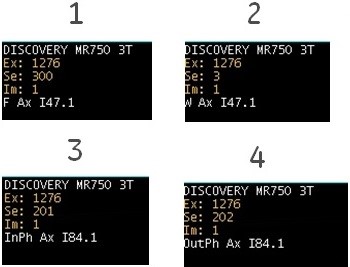
Table 1. Image legend Number Description 1, 2 The water-only and fat-only images are annotated as W or F, respectively. The effective TE is annotated as effective TE of the unshifted spin echo for 2D FSE and FSE with Imaging Option Fast Recovery (FRFSE-XL). 3, 4 The water+fat (in-phase) and water-fat (out-of-phase) images are annotated as InPh or OutPh, respectively. The effective TE is annotated as the corresponding fat/water in- or out-phase TE, and as the unshifted spin echo's effective TE for 2D FSE and FSE with Imaging Option Fast Recovery (FRFSE-XL) and Flex Imaging Option. - The success of spectral saturation techniques depends on the uniformity of the anatomical area being imaged, in addition to the pulse sequence and coil being used. While the system is shimmed to a system specification to provide you with optimal homogeneity, once a patient is placed in the magnet bore, the homogeneity can be affected. For example, an abdomen may be more uniform than a shoulder. It works best with anatomy of interest at isocenter, a small FOV, and no patient motion. In spite of careful patient positioning, all images within the Flex acquisition may not have complete fat or water suppression due to patient inhomogeneities such as areas in and around air cavities and metal implants, etc.
- The water image will have about 10 to 20% fat signal because the pulse sequence and processing used is more like the Classic fat saturation technique rather than the fat saturation technique.
CAUTION Images labeled as water may include signal from fatty tissue, and images labeled as fat may include signal from water. This error may occur in regions of high magnetic field variation, in spatially isolated tissue, due to patient or tissue motion, due to phase wrap artifacts, due to similar water and fat intensity in T2-weighted Flex scans, due to TE values beyond recommended limits, and/or in images with low signal-to-noise ratios. The presence of fat tissue in images labeled as water, or vice versa, may occur within single images or throughout an in entire stack of slices. By default, both sets of images (labeled fat and labeled water) will be reconstructed and inserted into the database for review. Proper calibration and center frequency selection will reduce the occurrence of this error. Complete elimination of this error may not be possible and thus interpretation of MR images must be completed by trained personnel. - The annotated NEX is different from the NEX value entered for the scan prescription. The annotated NEX reflects the value needed to optimize image quality and it is typically two times the NEX value entered (or three times for single-TR mode in 2D FSE and 3D Cube scans).
