- 00000018WIA30C22970GYZ
- id_400238801.2
- Feb 11, 2022 5:55:58 PM
Square Pixel
Square Pixel provides a square pixel within a rectangular FOV due to the selection of asymmetrical matrix values. The pixel size is determined by the FOV divided by the frequency matrix.
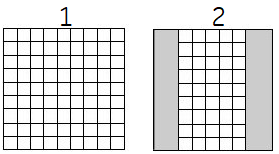
| Number | |
|---|---|
| 1 | Square Pixel turned off with a 256 frequency × 256 phase matrix |
| 2 | Square Pixel turned on with a 256 frequency × 192 phase matrix |
Use the Square Pixel Imaging Option when the anatomy in the phase direction is smaller than the new reduced FOV to reduce scan time and when you want higher spatial resolution with reduced scan times. The resolution is determined by the frequency axis of the matrix, and the scan time by the phase axis.
- Aliasing will occur when anatomy is outside the phase FOV. Use when anatomy in the phase direction is smaller than the new reduced FOV.
- For optimum image quality, use pads to raise the anatomy of interest as close to isocenter as possible. You want to position the anatomy as close to FOV center as possible because the FOV decreases evenly on both sides.
- Offset the FOV so that the anatomy is in the center of the screen to reduce the chance of aliasing.
- No Phase Wrap value greater than 1.0 is not compatible with Square Pixel.
- As the phase matrix value decreases, the SNR decreases.
- Select asymmetrical phase and frequency matrix values. There is a slight loss in SNR due to fewer phase steps applied when using Square Pixel. Compensate accordingly.
