- 00000018WIA30331870GYZ
- id_400253411.4
- Aug 19, 2022 12:48:41 PM
Respiratory Gating/Triggering
Respiratory Gating/Triggering reduces breathing artifacts by synchronizing the acquisition with the respiratory cycle. It can be used to acquire PD- or T2-weighted images. Data acquisition is generally completed during the quiet period of the breathing cycle. Respiratory Gating continuously applies RF at the defined TR time. Data acquisition only occurs during the Available Imaging Time, which is defined by the TP and TW.
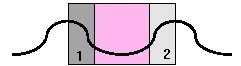
| Number | Description |
|---|---|
| Center area | AIT or Available Imaging Time |
| 1 | Trigger Delay |
| 2 | Trigger Window |
The Respiratory Tab becomes available when Respiratory/Gating Triggering is selected.
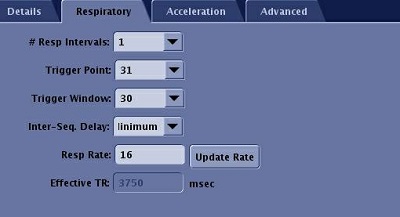
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| # of Resp Intervals | It determines the pulse sequence repetition time, or Effective TR. One respiratory cycle is the time from one maximum inspiration to the next maximum inspiration. |
| Trigger Point | Select or enter a Trigger Point value between 10 and 50%, which is the point in the respiratory cycle when imaging will begin. The goal is to set the trigger point and window so that the imaging window occurs at the quiescent portion of the breathing cycle. The TP does not affect available imaging time. |
| Trigger Window | Select or enter a Trigger Window value between 10 and 50%, which is the period from the end of the data acquisition window to the beginning of the next data acquisition window or the TP. The TW is the time set aside to stop data collection and allow for variations in the breathing pattern before the next TP occurs. Increasing the TW decreases the number of locations allowed because the available imaging time decreases. |
| Inter-Sequence Delay | Select an Inter-Seq. Delay time, in milliseconds, which is the time between each slice location in the respiratory cycle. Even spacing spreads slice acquisition time evenly across the available imaging time. Minimum spacing uses the smallest time possible to acquire the images within the available imaging time. |
| Respiratory Rate: Update Rate | Click to acquire an update of the patient's current respiratory rate in breaths per minute and view the value. |
| Effective TR | It is determined by the respiratory interval with gating. If the patient has a 4000 ms respiratory cycle, then the TR is 4000 ms. The Waveform indicates the respiratory triggers as tick marks along the bottom of the window. The window stays open when Respiratory Gating/Triggering is selected. |
Consider using Respiratory Gating/Triggering instead of Respiratory Compensation or breath-hold exams with very sick patients who cannot hold their breath or who do not have a consistent breathing pattern.
- Combined Cardiac/Respiratory Gating is allowed with:
- FastCard GRE/SPGR
- 3D Fast TOF
- Fast 2D PC
- 3D FGRE/FSPGR.
- Respiratory Gating/Triggering is not compatible with Respiratory Compensation.
- 2D mode and Respiratory Triggering are compatible with:
- DW EPI
- FSE
- FRFSE
- FSE-IR
- PROPELLER anatomy considerations
- SSFSE
- SSFSE-IR
- 3D mode and Respiratory Triggering are compatible with:
- Fast GRE/SPGR
- Fast TOF GRE/SPGR
- FIESTA
- FRFSE
- InHance 3D Velocity
- There is no form of respiratory arrhythmia rejection.
