- 00000018WIA30600970GYZ
- id_400254431.6
- May 4, 2022 2:28:41 AM
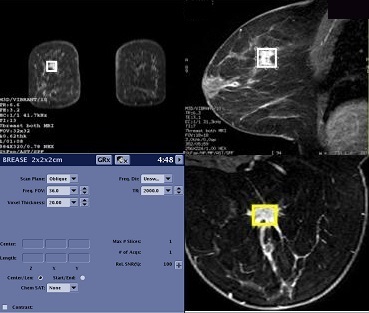
BREASE
About this task
Typically, BREASE is performed after first completing a study of the breast using VIBRANT. BREASE uses a TE-averaged, PRESS spectroscopy acquisition, compatible with the 4-, 7-, or 8-channel Breast coil.
Use these steps to acquire a BREASE spectrum for breast spectroscopy. The spectrum is displayed in the Viewer. MR breast spectroscopy can show if elevated concentrations of the Choline metabolite are present in a lesion.
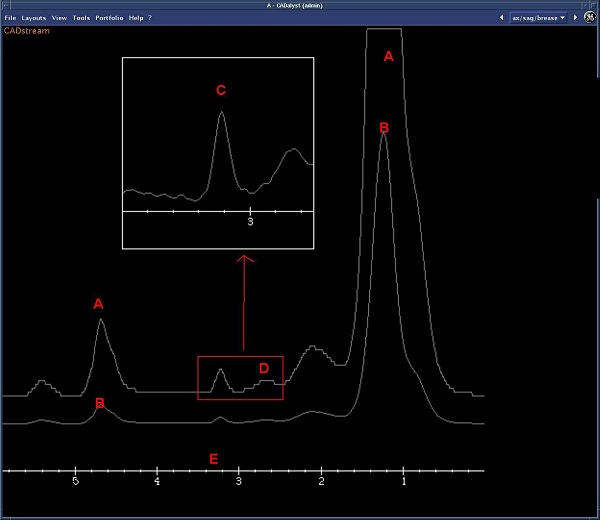
| Spectrum call out | Description |
|---|---|
| A | Spectrum A is a magnified version of spectrum B. |
| B | Spectrum acquired from BREASE VOI. |
| C | Zoomed spectrum from area D. Note that the zoom factor is fixed. |
| D | Represented by area C (zoomed). It is centered on the choline peak which is located, 3.2 ppm. |
| E | PPM scale. |