- 00000018WIA3068B770GYZ
- id_400243481.5
- Aug 14, 2022 6:34:03 PM
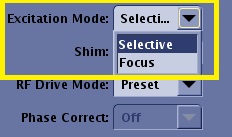
Excitation Mode
Select Excitation Mode to modify the type of the excitation RF pulse. Excitation Mode is located on the Scan Parameters Detail screen. The Excitation Mode menu only appears if a compatible application or PSD is currently selected.
There are three options. Only options available with the currently selected Application or PSD appear in the menu. If the menu selection is grayed-out, then it is the only option available and it is automatically applied.
Excitation Modes Selective and Non-Selective replace the old User CV Whole Volume Excitation.
- Whole Volume Excitation On = Non-Selective Excitation Mode.
- Whole Volume Excitation Off = Selective Excitation Mode.
Selective
Use Selective for routine scanning, which uses a selective excitation RF pulse. If Non-Selective and Focus are unavailable, the menu only displays a grayed-out Selective.
Non-Selective
Images are annotated: NSL in the lower left corner of the image and on the Series text page.
The User CV Whole Volume Excitation has been replaced with Excitation Mode Non-Selective.
Non-Selective is used with multiple PSDs:
- Multiple 3D PSDs and one-click Applications.
- 3D FSE PSDs such as Cube and Cube T2 FLAIR.
| PSD | Description |
|---|---|
| Non-Selective Excitation Mode is applicable for Sagittal and Coronal scans with many 3D Fast Gradient Echo Applications and PSDs. |
|
| Non-Selective Excitation Mode with Cube is used to reduce the shading or banding artifacts observed in some Cube images (acquired or reformatted). The Excitation RF, Readout Dephaser Gradient and Slice Rephaser Gradient are applied in a unique manner that results in reducing shading or banding artifact |
|
Focus
Use Focus to acquire brain, spine, body and extremity images with the following PSDs:
- 2D DWI and DTI
- 3D FSE
- 3D FRFSE-XL
- 3D CUBE
- 3D Cube T2 FLAIR
- 3D Cube DIR
Focus is an excitation method that can be combined with other MR acquisition techniques to image a reduced FOV. Compared with conventional RF excitation, Focus reduces the FOV in the phase encode direction within the imaging plane and does not cause the conventional phase wrap artifact. Focus is particularly useful in exams where the region of interest is small in the phase encode direction, for example spine, prostate and pancreas. The reduction in phase FOV can be achieved, for example, by 2D spatially selective excitation as in Focus DWI or with outer volume suppression as with Focus CUBE. For more details regarding Focus with Cube, see Cube and Cube T2 FLAIR scan.
The 2D RF pulse used by Focus DWI is sensitive to hardware delays, which can result in image degradation in areas that are far away from isocenter. The image degradation can manifest as poor signal homogeneity and/or dark bands in the image. Care should be taken to image close to iso-center in the phase and slice direction when possible.
Because of the sensitivity of EPI acquisitions to B0 inhomogeneities, placement of a local shim box around the region of interest is also highly recommended to achieve better image quality.

Image are annotated: FOC in the lower left corner of the image and on the Series text page.
Other PSD scan parameters, imaging options and saturation techniques are available if they can be selected; if not, they either don't appear or are grayed-out.
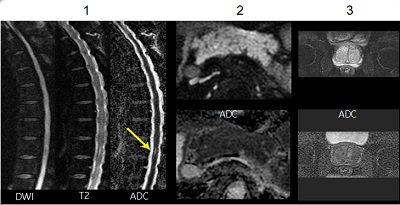
| Number | Description |
|---|---|
| 1 | DWI spine images with Focus. |
| 2 | DWI pancreas images with Focus. |
| 3 | DWI prostate images with Focus. |
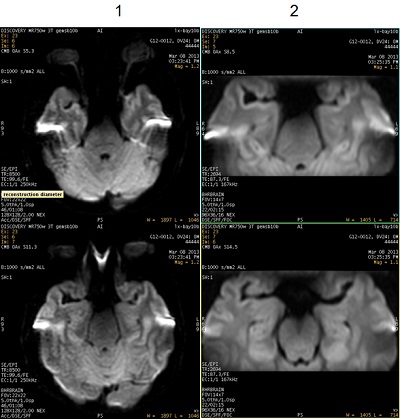
| Number | Description |
|---|---|
| 1 | DWI images acquired with Excitation Mode: Selective. Note the increased images magnetic susceptibility distortion effect. |
| 2 | DWI images acquired with Excitation Mode: Focus. Note the increased resolution due to less magnetic susceptibility distortion effect. |
