- 00000018WIA30A5A870GYZ
- id_400257801.5
- Aug 19, 2022 4:54:06 PM
Cube and Cube T2 FLAIR scan
Cube and Cube T2 FLAIR have a unique acquisition and reconstruction technique that allows for high resolution imaging in all three dimensions with the goal of acquiring isotropic voxels (all voxel dimensions, height, width, and depth, are equal). The advantage of acquiring isotropic voxels is that the data can be acquired in the plane that yields the greatest efficiency and then reformatted into any plane thus reducing the exam time. Images may be reformatted with slightly thicker slices (e.g., 3 mm) in order to improve SNR and reduce the number of images to be reviewed.
Use Cube to acquire high resolution imaging in all three dimensions with the goal of acquiring isotropic voxels (all voxel dimensions, height, width, and depth, are equal).
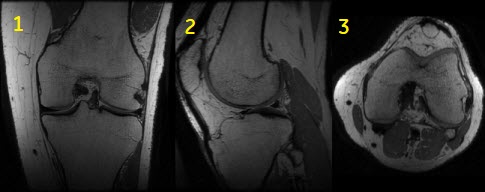
| Number | Description |
|---|---|
| 1 | Acquired coronal image |
| 2 | Reformatted sagittal image |
| 3 | Reformatted axial image |
By modulating the refocusing pulses’ flip angle, the range of image contrast is expanded from conventional FSE Fast Spin Echo applications.
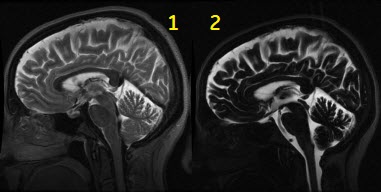
| Number | Description |
|---|---|
| 1 | Equivalent TE of 100 ms |
| 2 | Equivalent TE of 585 ms for hydrographic image contrast |
Consider this information when modifying Cube T2 or Cube T2 FLAIR scan parameters. For specific scan parameter values, select a protocol from your GE or Site library.
- Scan selections: 3D Mode, Fast Spin Echo family, Cube or Cube T2 FLAIR pulse, Extended Dynamic Range and IR Prepared Imaging Options.
General considerations
- Typically use Cube to acquire brain, C-spine, pelvis and knee images.
- When acquiring a Cube pelvis scan, it is recommended you acquire a sagittal or coronal plane. Acquiring an axial plane may result in annefact artifact.
- Images are annotated as M3D/Cube Pulse sequence/flip angle
- Graphically deposit and position a single slab.
Scan parameters
- Excitation Mode: When Non-Selective is available and the slice direction FOV is larger than the coverage, it is always recommended to use Non Selective Excitation. Non-Selective can result in improved SNR and decreased shading/banding artifact.
- Selecting Excitation Mode: Focus to reduce phase alias artifact when a small FOV is used.
Figure 3. Focus on/off comparison 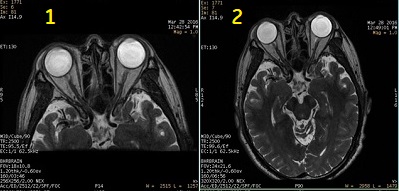
Table 3. Image legend Number Description 1 Small FOV with Focus 2 Large FOV without Focus - Focus is sensitive to B0 inhomogeneities and thus placement of a local shim box around the region of interest is highly recommended to achieve better image quality.
- When Focus is selected, the Phase FOV (on the scan parameter screen) can have a factor from 0.2 to 0.9. The phase acquisition matrix is automatically reduced proportionally to the phase FOV factor in the PSD.
- Scans should be planned carefully to keep in mind that reducing the FOV/phase FOV factor leads to SNR reduction.
- Selecting Excitation Mode: Focus to reduce phase alias artifact when a small FOV is used.
- No Phase Wrap: Use a value greater than 1.0 to reduce aliasing artifact for Cube and Cube FLAIR scans.
- SAT: Make selections for chemical saturation, as needed :
- None if you do not want to saturate the fat or water signal.
- Fat or Classic Fat to generate fat saturated images. Fat and Classic Fat are the same with the Cube application.
- Water to generate water saturated images.
- When either Fat or Classic Fat are selected, User CV Fat SAT Efficiency is available to control the amount of fat that is saturated.
- TE: It is typically not an editable field, but changing the bandwidth, resolution, and phase-FOV changes the TE. Cube pulse is compatible with Cube Enhance User CV. With Cube Enhance User CV = 2, consider the following to decide the proper TE value:
- The Minimum TE is 60 ms.
- The Maximum TE is determined by several scan parameters including: ETL, bandwidth, Frequency matrix and FOV.
- Increasing the ETL reduces scan time, but it also reduces SNR if the TE is much smaller than the Maximum TE.
- A lower ETL and maximum TE, in general, reduces blurring but increases scan time.
Imaging Options
- Acceleration: When using phased array coils, Acceleration is available. The recommended setting uses the maximum amount of acceleration in the phase and slice encode directions. Reduced acceleration factors result first in longer scan times, then longer echo trains, but with increased SNR. When higher SNR is needed, consider the following changes:
- reduce acceleration in the slice direction
- increase NEX value
- reduce the acceleration in the phase direction
- Cardiac Gating/Triggering: for Cube T2, Peripheral/Cardiac Gating is available for neuro imaging. The recommended delay time is designed to synchronize the acquisition with the low CSF-flow period of the cardiac cycle. Use the peripheral gating device to acquire the cardiac cycle.
- Extended Dynamic Range: it is always on and cannot be turned off. It is typically required for 3D acquisitions.
- Flex: enables a water-fat separation technique that can used in place of conventional fat saturation to produce water-only images.
- Flow Compensation: if it is prescribed with a Cube scan, Excitation Mode selected from the scan parameters Detail screen is set to Selective. Non-Selective is not compatible with Flow Compensation and Cube.
- HyperSense: use with ARC to acquire faster (30- 50% scan time reduction) in multiple body regions.
- IR Prepared: when the sequence Cube-T2FLAIR is selected, IR-Prep is automatically selected and the TI is automatically calculated to null CSF.
- MDSE considerations: Combine Cube with MDSE Imaging Option for vessel wall (plaque) imaging.
- ZIP 512: it is always recommended for Cube acquisitions.
- T1FLAIR: use to provide better T1 contrast with suppressed CSF.
Figure 4. Cube comparison with and without T1 FLAIR Imaging Option 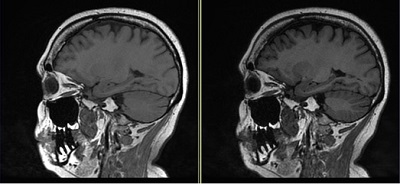
Table 4. Image legend Image Description Left Cube image with no T1 FLAIR Imaging Option. Right Cube with T1 FLAIR Imaging Option demonstrates better gray matter/white matter contrast in comparison to Cube T1 image.
User CVs
Click the Advance tab to view the available User CVs. The CVs may vary based on the field strength and selected scan and imaging parameters.
- Apodization Level
- Cube Enhance
- It can be used to customize the internal Cube parameters to produce particular contrast for specific anatomy.
- CV Cube Enhance set to 3 (Brain T1) can produce 3D isotropic images with reduced artifacts in comparison to a traditional 2D Spin Echo scan. However, residual flow artifacts and ringing artifact may still be present.
- Cube Enhance STIR
- Center K refocusing flip angle
- It can be used to reduces image blurring with a tradeoff of reduced SNR. This is only available if Cube Enhance User CV is set to 1 (MSK).
- Fat Saturation efficiency
- Fast Single TR Bipolar Acquisition
- It is available when Flex Imaging Option is selected.
- Reformat Optimization
- SAR Optimization
- Slice Partial Fourier
Post-process tasks
There are multiple compatible post-process tasks. For details, see Add post-process task.
- Maximum Intensity Projection
- Multi Planar Reconstruction
- Image Enhancement Filters
- Pasting
- Reformat tip: To improve SNR and reduce the number of images in each series, the reformats may be designed to be thicker than the source images. For example, 3 mm with 1 mm overlap. To program an overlap, select a value for the Spacing Between Views that is less than the slice thickness. To change the Spacing Between Views, from the Reformat control panel, click . The slice thickness is red text on the reformatted image.
