- 00000018WIA30BBE870GYZ
- id_400244551.5
- Aug 15, 2022 7:27:48 PM
Phase FOV
Select a Phase FOV to reduce phase steps and thus reduce scan time. Use a small Phase FOV for scans with anatomy smaller than the FOV in the phase direction, such as extremities, spines, axial, and coronal heads. Also use a reduced Phase FOV for high resolution images in a short scan time when combined with a symmetrical matrix.
- Decrease the Phase FOV and Signal-to-Noise Ratio (SNR) is reduced by approximately: – 14% for 0.75 Phase FOV, – 30% for 0.5 Phase FOV.
- Decrease the Phase FOV in Echo Planar Imaging (EPI) acquisitions to decrease geometric distortion and increase spatial resolution.
- Phase FOV requires more precise placement of anatomy in the center of the Field Of View (FOV). This is easily accomplished with FOV center offsets.
- Phase wraparound occurs if anatomy exists outside the new, reduced FOV. SATuration Pulse (SAT) pulses placed in the phase direction can reduce the aliasing artifact.
- Typically a Phase FOV less than one is not selected on a sagittal or coronal if phase and frequency are swapped.
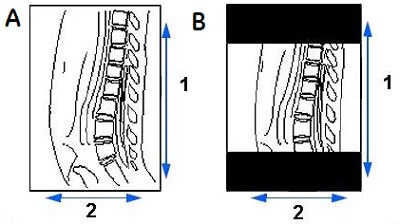
| Callout | Description |
|---|---|
| 1 | Phase |
| 2 | Frequency |
| A | Phase and Frequency swapped with a Phase FOV of 1 |
| B | Phase and Frequency swapped with a Phase FOV of 0.75 |
Spectroscopy Phase and Frequency selections
- PROBE SV: phase and frequency values must = 1.
- PROBE SI: Acceptable values are even numbers 8 to 24. (FOV ÷ phase value) × (FOV ÷ frequency value) × Voxel Thickness value = CSI grid voxel.
- 3D CSI: Acceptable values are even numbers 8 to 16. As the phase and frequency values increase, the spatial resolution and the scan time increase. (FOV ÷ phase value) × (FOV ÷ frequency value) × CSI Slice Thickness value = CSI grid voxel.
