- 00000018WIA304F3970GYZ
- id_400270811.4
- Aug 20, 2022 11:49:43 AM
Fast GRE scan
FastGRE uses variable flip angles to excite protons, then rephases them by means of gradients. Compared to the conventional GRE sequence, the Fast GRE sequence uses a shorter duration excitation RF pulse and a wider receive bandwidth that shortens the duration of the readout time. This implementation allows the prescription of shorter TRs and TEs and therefore shorter total scan times.
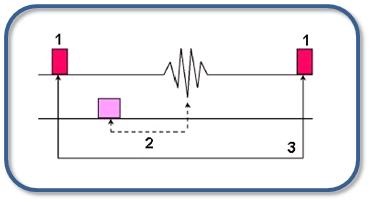
| Number | Description |
|---|---|
| 1 | Fractional RF |
| 2 | TE |
| 3 | TR |
Fast GRE sequences are used to produce T2-weighted images. Tissues with short T2 are dark and tissues with long T2 are bright. In the brain, CSF produces the brightest signal on moderate to late TE images.
Consider this information when modifying Fast GRE scan parameters. For specific scan parameter values, select a protocol from your GE or Site library.
- Scan selections: 2D or 3D Mode, Gradient Echo family, Fast GRE pulse.
- Scan selections for MENSA, a hybrid T2/T1 (FIESTA) and T2 contrast with musculoskeletal scan: 3D Mode, Gradient Echo family, Fast GRE pulse, Pulse Name type-in field: mensa. Note that only an even number of slices per slab is allowed.
General considerations
- The Fast GRE sequences result in reduced SNR when compared to non-fast GRE sequences. The SNR decrease results from the use of: higher bandwidths, ultra-short TR values, fractional NEX, and fractional echo.
- Chemical shift effects are seen when a voxel contains both fat and water and the TE is timed for the vectors to be in or out of phase. Boundary between fat and tissues with much water are either bright or dark.
Scan parameters
- TR: Due to the short TRs, saturation effects occur resulting in a reduction in SNR and CNR. Short TRs do not allow flip angle flexibility to manipulate image contrast because increasing the flip angle can produce greater saturation effects.
- NEX: Increasing NEX to improve SNR may not be an option because of the increased scan time.
Imaging Options
- SR Prepared: Select it to provide contrast for hypo-perfused regions of the myocardium.
- Motion Compensation: Select it to reduce respiratory motion and residual cardiac motion. For details, see Motion Compensation considerations.
- Respiratory Trigger: When it is on, the available imaging time is segmented by the Min TR. It is used to acquire as many phase and slice encodings as possible that will fit in the available imaging time for one respiratory interval.
3D only considerations
- For 3D dual echo scans, when TE range reaches it’s in/out of phase limits some imaging parameters are restricted.
- Up to 10,000 images can be acquired within a single 3D Fast GRE series.
- Because the 3D dataset is acquired over multiple respiratory intervals, it is recommended that a larger Trigger Window (60%) be used to acquire as much data as possible between respiration’s.
- To reduce excessive ghosting with a 3D sequence, consider using a NEX integer when the No Phase Wrap value is greater than 1.0.
User CVs for 3D
Click the Advance tab to view the available User CVs. The CVs may vary based on the field strength and selected scan and imaging parameters.
