- 00000018WIA30C46970GYZ
- id_400219181.3
- Aug 21, 2022 6:01:14 PM
TOF: 3D GRE/SPGR scan
3DTOF uses a volume acquisition to obtain image data and it can be acquired with a GRE or SPGR pulse.
Use 3D TOF-GRE and TOF-SPGR for:
- AVMs
- aneurysms of the Circle of Willis
- intracranial carotid occlusive disease
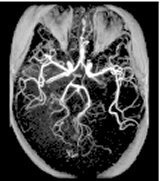
Consider this information when modifying 3D TOF GRE/SPGR scan parameters. For specific scan parameter values, select a protocol from your GE or Site library.
- Scan selections: 3D mode, Vascular family, TOF-GRE or TOF-SPGR pulse.
General
- It provides lower blood-background CNR.
- It is only effective for relatively small volumes
- It results in less overestimation of stenosis than with 2DTOF, due to low dephasing.
- It may make short T1 structures appear bright, simulating flow enhancement.
- It discards two slices on either end of the imaging volume due to slice aliasing.
- 3DTOF is sensitive to fast and intermediate flow. It is less sensitive to slow flow, which may become saturated as it passes through the imaging volume (the use of Ramp Pulses can offset some of this saturation).
- 3D TOF generates source, collapsed, and projection images.
Scan parameters
- Flip angle: Due to reduced minimum TR values (in particular with Magnetization Transfer), the flip angle may be decreased to minimize saturation of small vessels.
- Stationary spins are suppressed if the flip angle is 15 to 20°. The larger the flip angle, the more saturated stationary tissue becomes, but large flip angles can affect the arterial flow, resulting in a lower signal intensity.
- Overlap: To reduce venetian blind artifact, prescribe a minimum Overlap Locs that is 25% of the Slices per Slab.
- Projections images: Deselecting projection images (i.e., selecting 0 projections on the TOF tab) substantially increases the reconstruction speed. This can be useful with the ZIP 512 Imaging Option.
- Ramp pulses: Select Ramp pulses from the TOF tab to increase conspicuity of intracranial arteries.
- SAT: If 3D TOF is used with either Fat SAT (Fat selected from the Chem SAT menu on the Scan Parameters screen) or Magnetization Transfer Imaging Option and SAT, a NEX value less than 1 is available.
- Slabs: Multiple, smaller slabs decrease saturation of slow moving and in-plane flow. Increasing the number of slabs and increasing scan time. Prescription of slabs outside the localizer FOV is not allowed.
- Slice thickness: Thin slices combined with Flow Compensation increase the minimum TE value, and maximize in-flow enhancement, therefore decreasing the effects of in-plane flow.
- TE: Very short TEs reduce the amount of spin dephasing.
- TR: As TR decreases, background tissue saturation increases and signal from blood can decrease as it moves through the imaging volume. Selection of a TR that is too short (< 33 ms) can result in suppression of smaller vessels. Due to low minimum TR values (in particular with Magnetization Transfer), the flip angle may be decreased to minimize saturation of small vessels.
Imaging Options
- HyperSense: When 3D TOF is used without HyperSense Imaging option, the NEX value = 0.85, which is a partial Fourier Ky technique to decrease scan time.
- Magnetization Transfer: If 3D TOF is used with Magnetization Transfer Imaging Option and SAT, a NEX value less than 1 is available.
- Use it to improve contrast between blood flow and surrounding tissue.
- The minimum TR with the Magnetization Transfer Imaging Option is shorter with transmit/receive coils other than the body coil.
User CVs
Click the Advance tab to view the available User CVs. The CVs may vary based on the field strength and selected scan and imaging parameters.
- Apodization Level
- PURE compensation
- Ramp Sampling
- Vessel Uniformity
- It can make vessels more uniform in appearance.
Post-process tasks
There are multiple compatible post-process tasks. For details, see Add post-process task.
- Image Enhancement Filters
- Maximum Intensity Projection
- Multi Planar Reconstruction
- Pasting
