- 00000018WIA30946970GYZ
- id_400247391.3
- Aug 21, 2022 5:48:23 PM
TOF: 2D GRE/SPGR scan
2DTOF completes data acquisition for one slice before moving on to subsequent slice locations. Images can be acquired using a TOF-GRE or TOF-SPGR sequence. TOF imaging acquires one phase encoding value per TR period. A variable angle RF excitation pulse, gradient rephasing, and flow compensation are used in these sequences.
MRA images are created by repeatedly exciting a predefined volume of anatomy until the stationary tissue is partially saturated and the signal from the tissue is suppressed. Blood flowing into the predefined volume of anatomy is not saturated but fully magnetized by the main magnetic field and yields a stronger signal. In the resulting image, the blood appears bright and the stationary tissue is suppressed. This phenomena is called a flow-related enhancement.
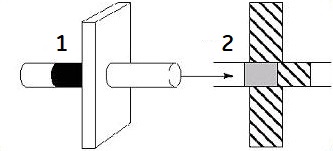
| Number | Description |
|---|---|
| 1 | TOF imaging |
| 2 | Flow |
Use 2D TOF-GRE and TOF-SPGR sequences to:
- demonstrate the carotid bifurcation or venous anatomy
- evaluate suspected basilar artery occlusive disease
- Image pelvic and lower extremity vasculature
- map cortical veins
- evaluate suspected intra-cranial venous thrombosis
Consider this information when modifying 2D TOF GRE/SPGR scan parameters. For specific scan parameter values, select a protocol from your GE or Site library.
- Scan selections: 2D mode, Vascular family, TOF-GRE or TOF-SPGR pulse.
- For ungated peripheral run-off exams, select a 2D TOF GRE or SPGR pulse sequence and type 2dtofx in the PSD name field, which optimizes the SAT gap to improve the background suppression. The default value for the spatial SAT gap is 10 mm.
General
- TOF is a an imaging technique that relies primarily on flow-related enhancement to distinguish moving from stationary spins in creating MR angiograms. Blood that has flowed into the slice has not have experienced RF pulses and therefore appears brighter than stationary tissue.
- It is sensitive to slow flow or moderate flow.
- There are minimal saturation effects at normal flow velocities.
- TOF-GRE uses a non-RF spoiled gradient echo technique, therefore increased T2* effects may be noted.
- TOF-SPGR uses RF spoiling to minimize residual transverse magnetization to optimize T1-weighting.
- 2D TOF acquisitions have the potential for overestimating stenosis because the minimum TE is relatively long in comparison to 3D TOF.
- Patient motion can result in misregistration of the acquired slices when viewed in projection.
Scan parameters
- SAT: Select spatial SAT pulses perpendicular to the flow and in a direction that reduces unwanted flow.
- To suppress venous flow above the heart (head and neck exams) use a superior SAT pulse, and to suppress venous flow below the heart use an inferior SAT pulse.
- TI: Simulated flow-related enhancements can result from short T1 substances like methemoglobin in subacute hematomas and some clots.
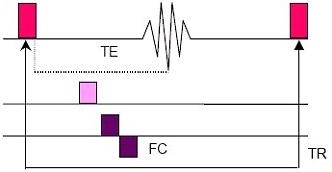
- TE: As the TE gets shorter, sensitivity to very fast in-plane and turbulent blood flow increases, and signal loss and artifacts decrease.
- Thin slices combined with the Flow Compensation Imaging Option increase the minimum TE value and maximizes in-flow enhancement, therefore decreasing the effects of in-plane flow.
- TR: Short TR suppresses the signal from stationary tissue and maximizes the vessel contrast due to flow related enhancements.
Post-process tasks
There are multiple compatible post-process tasks. For details, see Add post-process task.
- Image Enhancement Filters
- Maximum Intensity Projection
- Multi Planar Reconstruction
- Pasting
