- 00000018WIA30DE7870GYZ
- id_400259541.5
- Aug 11, 2022 1:09:22 PM
Annefact artifact
To suppress annefact artifacts in 3D Vascular Fast TOF scans, see Annefact Reduction for details. Annefact is a peripheral signal artifact that appears as ribbons of signal smeared through the image. This artifact is caused from signals generated outside the desired FOV that are detected by the receiver. Annefact appears in FSE scans as smeared, bright, ghosting signals through the image in the phase direction. It typically appears on sagittal spines or pelvis scans using a phased array surface coil. Like a Star artifact, its origin is far from isocenter, where the gradients are non-linear. Uncompensated eddy currents in this area cause phase errors in the compressed signal and smear it through the image.
Methods to prevent or reduce the incidence of the annefact artifact include:
- Select the receive coils that match the imaging FOV (i.e., LS45, LS56, CS12, etc.), which lessens the likelihood of picking up the peripheral signals that are generated outside the FOV.
- Verify the frequency is set to S/I for sagittal spine imaging.
- Place a SAT band anterior to the spine.
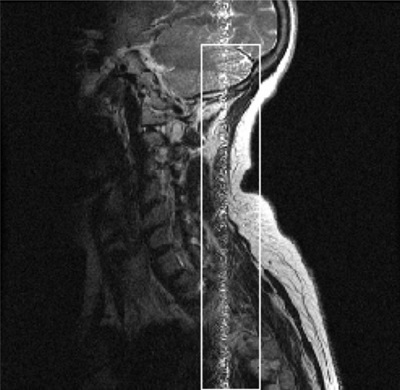
The following FSE sagittal cervical spine image displays an annefact. The image was acquired with a 24 cm FOV and the phase and frequency swapped. The artifact could have been prevented by not swapping phase and frequency and using a 2-coil selection, such as CS12 so the surface coil coverage would closer match the scan FOV.
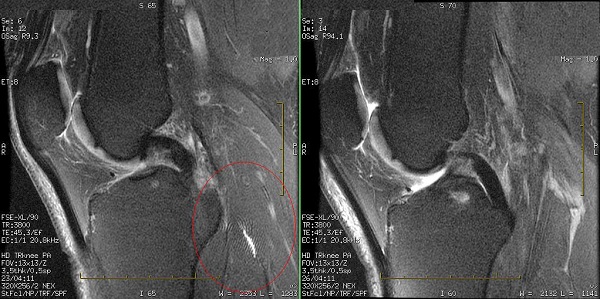
If the HD Knee Array coil is placed at isocenter, an annefact artifact can appear on the sagittal or coronal knee images. Therefore, place the HD Knee Array coil right or left off-center by approximately 60 to 70 mm (the positioning range is 60 to 120 mm).