- 00000018WIA30ECE770GYZ
- id_400217631.4
- May 5, 2022 3:57:36 PM
Cardiac introduction
Cardiac Gating/Triggering allows the same data to be collected at the same points of the cardiac cycle for each repetition of the pulse sequence allowing motion artifacts to be reduced, or sometimes eliminated. The benefit is that the motion is always the same and is essentially “frozen,” allowing motion artifacts to be reduced or, sometimes, eliminated. Gating and triggering of MR images can be performed with ECG or Peripheral gating techniques.
| Scan plane | Cardiac application |
|---|---|
| Short Axis | Assesses two chambers, either both atria or both ventricles. |
| 2-Chamber Long Axis | Visualizes left atrium mitral valve and left ventricle. |
| 4-Chamber Long Axis | Assesses septal wall and visualizes the four chambers, mitral, and tricuspid valves in a single plane. |
| 3-Chamber View (left ventricular out-flow tract) | Assesses left atrium, mitral valve, left ventricle, aortic valve, and aortic root in one plane. |
Cardiac Triggering
Cardiac triggering is a technique that turns RF application and image acquisition on and off based on a trigger detected within the cardiac or respiratory cycle. The Trigger Window is set as a percentage of the cardiac (or respiratory) cycle. Trigger Delay is usually set to minimum to minimize acquisition delays, unless the application requires it. Triggering synchronizes data acquisition with the waveform cycle, and all image data is acquired at the same phase in the cycle for each slice prescribed.
Spin Echo, Fast Spin Echo, Fast GRE-ET, and multi-planar 2D GRE/SPGR sequences use Cardiac Triggering.
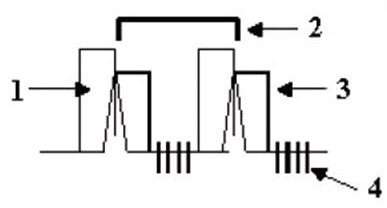
| Number | Description |
|---|---|
| 1 | Trigger Window |
| 2 | RR Interval |
| 3 | Trigger Delay |
| 4 | Slices |
Cardiac Gating
Cardiac gating monitors the cardiac or respiratory cycle, but does not use a trigger to initiate RF application. RF is applied throughout the cycle at the defined TR, and data is acquired when the desired physiological event occurs.
Fast Card, FastCINE, 3D Fast GRE/SPGR, 3D Fast TOF (GRE/SPGR), FIESTA, and Fast 2D PC use Cardiac Gating.
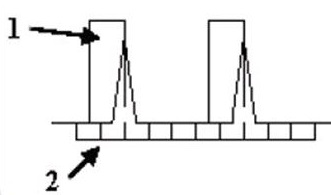
| Number | Description |
|---|---|
| 1 | Trigger Window |
| 2 | Uniform TR |
Cardiac and respiratory gating/triggering
The following pulse sequences allow the use of Combined Cardiac and Respiratory Gating/Triggering: 3D Fast Gradient Echo, Fast Card, and FastCINE sequences.
If a valid ECG trigger is detected within the respiratory data acquisition window, scanning begins. When the end of the data acquisition window is reached, scanning stops. RF application is continuous, being applied at the TR time throughout the entire respiratory cycle, even when the data acquisition window is closed.
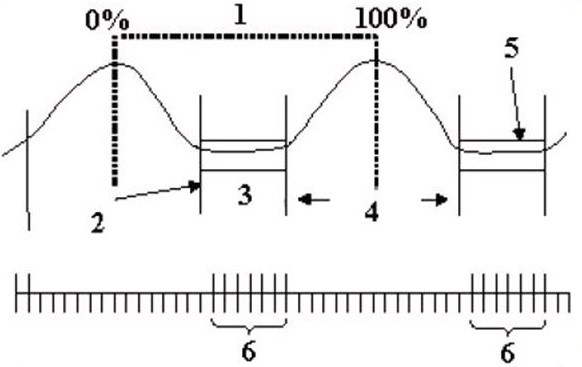
| Number | Description |
|---|---|
| 1 | One respiratory cycle from 0-100% |
| 2 | Trigger Point of 30% |
| 3 | Time frame when cardiac gated slices are acquired |
| 4 | Trigger Window |
| 5 | Time frame when cardiac gated slices are acquired |
| 6 | Slices |
