- 00000018WIA30956970GYZ
- id_400268011.1
- Feb 24, 2022 5:14:59 PM
2D CINE
This topic considers the differences between Retrospective CINE (FastCINE) and Prospective CINE (FastCard).
Retrospective CINE
- Scan selections: Oblique mode, Vascular family, Fast 2D Phase Contrast pulse, Flow Compensation, ASSET and Sequential Imaging Options.
- Scan selections: 2D mode, Gradient Echo family, Fast SPGR, Fast GRE, or FIESTA pulse.
- with FIESTA select these Imaging Options: Cardiac Gating/Triggering, ASSET, ZIP512
- with Fast SPGR select these Imaging Options: Cardiac Gating/Triggering, Flow Compensation, Sequential, ZIP512
- with Fast GRE select these Imaging Options: Cardiac Gating/Triggering, Flow Compensation, Sequential, ZIP512
Retrospective CINE (or FastCINE) is a prospectively gated scan and retrospectively reconstructed. The prospective gating means that new k-space lines are acquired every time the system receives a new trigger. Retrospective reconstruction means that the number of TRs per RR interval (heartbeat) can vary and data is sorted in reconstruction (retrospectively or after the scan is done). Data acquisition is done continuously and, if arrhythmia rejection is selected, data is rejected and reacquired when a new R-peak occurs that is outside the Arrhythmia Rejection Window (ARW).
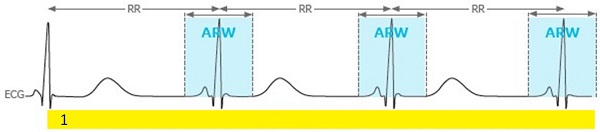
| Legend | Description |
|---|---|
| RR | R-peak to R-peak of ECG cycle |
| ARW | Arrhythmia Rejection Window |
| 1 | Yellow bar represents data acquisition |
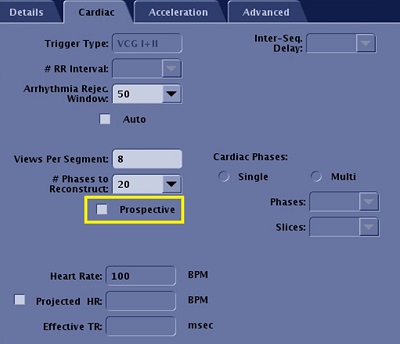
Activate Retrospective gating or FastCINE
Do not select the Prospective option box on the Cardiac tab.
Retrospective CINE Arrhythmia Rejection behavior
- For retrospective CINE arrhythmia rejection takes into account short and long arrhythmias (in case arrhythmia rejection is on, CV = 1 or2).
- Arrhythmia Rejection Window (ARW) is defined as a percentage of the RR interval (taken from the Heart Rate at the moment of scan or Projected Heart Rate if used) in the cardiac tab. ARW is only used for arrhythmia rejection management if CV0 is set to 1 or 2.
- RR intervals will be marked as arrhythmic if the following occurs:
- If the RR interval is less than RR minus ARW*RR.
- If the RR interval is greater than RR plus ARW*RR.
- All RR intervals in between RR plus/minus ARW*RR will be considered good. For example, given a heart rate of 60 BPM (corresponding to an RR interval of 1000ms) and ARW of 20%, then RR intervals outside of the 800ms-1200ms range will be rejected
- Arrhythmia rejection has 3 modes in retrospective CINE:
- CV0 = 0 Disconnected: It collects all data independently of the value of arrhythmia window in the cardiac page. It assumes all data is good.
- Advantage: Scan will complete during the expected time.
- Disadvantage: If there are arrhythmias or bad triggering happens during the acquisition, image quality will be compromised because all collected data will be assumed to be good.
- CV0 = 1 Non-threshold mode: Rejects all RR intervals that are not within the defined RR ±arrythmia rejection window and thus the scan continues until all views are collected.
- Advantage: Scan will not be stopped so images will be created.
- Disadvantage: Breathhold time could be very long, and image quality can be degraded due to patient breathing.
- CV0 = 2 Thresholded mode: Rejects a maximum of XX RRs (XX is a fixed value that depends on the acquisition time, for <25 seconds it is 8 and for >25 seconds it is 20). The scan then stops and the status is shown on the up right corner of the main screen: “scan done: Action Failed”. A foot note appears to show why it failed: "Timed out. No valid triggers for 10 secs due to arrhythmia or loss of ECG signal".
- Advantage: It prevents breath holds from becoming too long.
- Disadvantage: Scan is stopped and no images are reconstructed.
- CV0 = 0 Disconnected: It collects all data independently of the value of arrhythmia window in the cardiac page. It assumes all data is good.
-
Note: that if arrhythmia rejection is on, CV0=1 or 2, the scan also stops if during 10 CONSECUTIVES seconds a proper trigger within the arrhythmia rejection window is not received.
Prospective CINE
- Scan selections: 2D mode, Gradient Echo family, Fast SPGR, Fast GRE, or FIESTA pulse.
- with FIESTA select these Imaging Options: Cardiac Gating/Triggering, ASSET, ZIP512
- with Fast SPGR select these Imaging Options: Cardiac Gating/Triggering, Flow Compensation, Sequential, ZIP512
- with Fast GRE select these Imaging Options: Cardiac Gating/Triggering, Flow Compensation, Sequential, ZIP512
Prospective CINE (or Fastcard) is prospectively gated but contrary to Cine it always acquires the same number of TRs per RR interval and then it stops acquiring data, while maintaining the RF to keep the steady state, until the next trigger is detected. The acquisition time per RR is always less or equal to the RR interval of the patient at the moment of the sequence download.
- Only use prospective CINE when retrospective CINE is not possible, for example with patients that have very arrhythmic heart beats.
- When using prospective gating, select arrhythmia rejection On (Advanced tab, CV0 = 1) and prescribe a Projected HR that is the patient's highest heart rate.
- For example, in a very arrhythmic patient whose heart rate oscillates between 50 and 100 bpm, set Projected HR to 100 and turn on arrhythmia rejection. The available image time will be 600 ms. If during the scan, the patient has a couple of cycles with heart rate 120 bpm, these data will be rejected and reacquired.
- If the heart rate becomes faster and more than four arrhythmias occur, the scan will stop. Repeat the scan after increasing the value of Projected HR to the new highest HR of the patient.
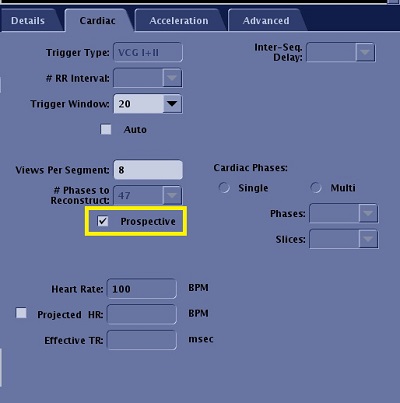
Activate Prospective gating or FastCard
Select the Prospective option box on the Cardiac tab.
Prospective CINE Available Image Time and Arrhythmia Rejection
- In Prospective CINE, data acquisition is done during Available image time, which it is calculated differently if arrhythmia rejection is set to on or to off (CV0 in Advanced CVs).
- In prospective gating, Trigger Window (TW) is defined as a percentage of the RR interval (taken from the Heart Rate at the moment of scan or Projected HR if used) in the cardiac tab such that the acquisition time is always less than the RR interval. During the trigger window data is not acquired, the pulse sequence keeps playing RF pulses to maintain steady state.
- When arrhythmia rejection is off: Available image time is the RR interval in the scan (or the RR interval corresponding to the projected heart rate manually set) minus Trigger window (TW) * RR interval.
- When arrhythmia rejection is on: Available image time is the RR interval in scan (or the RR interval corresponding to the Projected HR manually set) independently of the value of TW.
- Arrhythmia rejection has 2 modes in prospective CINE:
- CV0 = 0 Disconnected: It collects all data during available image time.
- Advantage: If the projected heart rate is set high enough so that there is no new trigger within the available image time, systolic CINE images could be acquired with good IQ.
- Disadvantage: If there are arrhythmias or bad triggering happens during the acquisition, image quality will be compromised because all collected data will be assumed to be good.
- CV0 = 1 Thresholded mode: It rejects a maximum of XX RRs (XX is a fixed value that depends on the acquisition time, for <25 seconds it is 4 and for >25 seconds it is 10). The scan then stops and the status is shown on the up right corner of the screen: “scan done: Action Failed”. A foot note appears indicating why it failed: "Timed out. No valid triggers for 10 secs due to arrhythmia or loss of ECG signal."
- Advantage: It prevents breath holds to become too long while handling arrhythmia.
- Disadvantage: Scan is stopped and no images are reconstructed.
- CV0 = 0 Disconnected: It collects all data during available image time.
-
Note: If arrhythmia rejection is on, CV0 = 1, the scan also stops if during 10 CONSECUTIVE seconds a proper trigger within the arrhythmia rejection window is not received.
- Arrhythmia Rejection OFF
- Projected HR=60
- TW=20%
- Available Image time = 800 ms
Figure 4. ECG waveform of Prospective CINE with Arrhythmia Rejection OFF 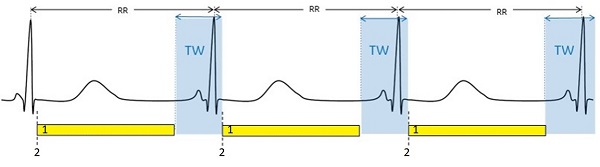
Table 2. Image legend Legend Description RR R-peak to R-peak of ECG cycle TW Trigger Window 1 Yellow bar represents data acquisition or available imaging time (AIT) 2 Trigger detected - Arrhythmia Rejection ON
- Projected HR=75
- Available Image time = 800 ms
Figure 5. ECG waveform of Prospective CINE with Arrhythmia Rejection ON 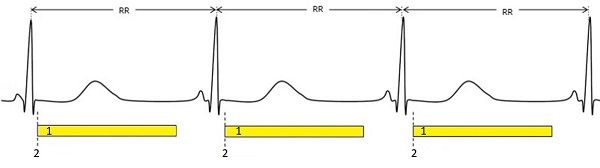
Table 3. Image legend Legend Description RR R-peak to R-peak of ECG cycle TW Trigger Window 1 Yellow bar represents data acquisition or available imaging time (AIT) 2 Trigger detected
