- 00000018WIA30A6C870GYZ
- id_400237731.4
- Aug 19, 2022 2:25:29 PM
Spin Echo EPI
EPI uses multiple oscillating gradient “pulses” within a TR period, rather than RF to create the echo. A SE EPI protocol produces contrast similar to a standard SE image with the same TR and TE.
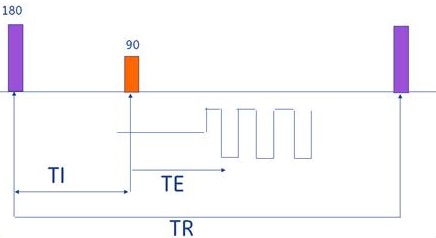
SE EPI is typically used to acquire T2-weighted scans. It can also be combined with the IR Prepared Imaging Option to acquire T1-weighted or IR images.
Consider this information when modifying Spin Echo EPI scan parameters. For specific scan parameter values, select a protocol from your GE or Site library.
- Scan selections: 2D Mode, Echo Planar Imaging family, Spin Echo EPI pulse.
Spin Echo EPI applications include:
- Acquiring very fast T2 (SE-EPI) contrast when short scan time is imperative; e.g., to minimize breathing motion, or motion from patients that cannot hold still.
- Imaging pathologies that cause disruptions in the local magnetic field because they have a higher potential for contrast visualization with EPI sequences.
- Cardiac imaging for single-slice multi-phase cardiac image without using gating. A single shot acquisition images at a single location over a period of a few seconds.
- Single or multi-slice multi-phase using cardiac gating taken within a single breath hold.
- Acquiring very fast T1-weighted images by adding IR Prep, using a long TR (2000 ms), a TI to produce T1 contrast (to 800 ms), and a short TE. These images have a fat suppression appearance due to the spectral fat suppression technique and are typically used in head and extremity imaging.
General considerations
- Up to 10,000 images can be acquired within a single EPI multi-phase series.
- There are two EPI type-in PSDs compatible with SE EPI and GRE EPI. For details, see Gradient Echo EPI.
- When using the head coil, axial, axial oblique, coronal, and coronal oblique, planes automatically have the phase and frequency swapped, in comparison to non-EPI scans. This is to lessen the presentation of geometric distortion and to reduce the potential for peripheral nerve stimulation.
Scan parameters
- Bandwidth: As the RBw increases, SNR decreases, chemical shift artifact decreases, minimum TE decreases (which means the ESP decreases). As ESP decreases, geometric distortion decreases.
- 64 kHz is used with 4 to 8 shots.
- RBw > 64 kHz depends on balancing ESP and resolution demands.
- Single-shot EPI uses the largest RBw possible.
- FOV: Large FOVs decrease resolution, increase SNR, and decrease echo space.
- Frequency: As the frequency matrix increases, the ESP increases.
- The shortest possible ESP is desirable for a single shot acquisition. Therefore, as the # of shots decreases, consider increasing the FOV.
- Typically on a single-shot, keep the frequency matrix as low as possible to keep the ESP as short as possible. Finding the right balance between ESP and resolution is critical.
- Typically a 256 frequency matrix is used with 8 shots or more and RBw 32 to 64 kHz. For 512 frequency matrix, increase the shots and RBw.
- Phase: As phase matrix increases, the resolution increases, and the # of slices decreases, but the scan time does not change, (scan time = shots × TR). An EPI protocol is the only instance where phase may be larger than the frequency value.
- Phase Correct: Always select Phase Correct with EPI scans so that the system can run a “reference” scan prior to data acquisition.
- If a 1 NEX acquisition is programmed, the reference scan can take as long as the EPI scan, but it is imperative to run Phase Correct in order to have optimum image quality.
- The reference scan automatically occurs after a successful prescan. It makes calculations and corrections for placing the echo underneath the frequency gradient.
- Phase FOV: As PFOV decreases, geometric distortion decreases.
- Shots: As the number of shots increase, the susceptibility artifacts decrease, and the scan time increases.
Imaging Options
- IR-Prepared: Select it for either an IR, T1-weighted, or STIR contrast image.
User CVs
Click the Advance tab to view the available User CVs. The CVs may vary based on the field strength and selected scan and imaging parameters.
- Ramp Sampling
- When the Ramp Sampling is turned on, the RBw is automatically set.
- Spectral-Spatial FatSAT
- On wide bore systems, consider setting Maximum Number of Slices Optimization to 1 to increase the number of slices per acquisition at the expense of increased echo space and geometric distortion.
Post-process tasks
For details, see Add post-process task. Compatible post-process tasks include:
- Image Enhancement Filters
- Negative Enhancement Integral: MRSTD with Multi-Phase and fMRI Imaging Options
