- 00000018WIA30848970GYZ
- id_400237061.4
- Apr 13, 2022 9:53:33 AM
Diffusion Weighted Imaging
READY View Diffusion Weighted Imaging generate parametric images from a Diffusion Weighted data set.
READY View has algorithms to process DWI images to generate ADC and eADC maps to eliminate T2 “shine through” in the isotropic (trace) DWI. The ADC algorithm subtracts the T2 information from the DWI image. The Ratio (eADC) map is a relative inverse of the ADC map.
- In an isotropic DWI image, restricted diffusion is bright and T2 “shine through” is bright.
- When ADC is applied, restricted diffusion is dark and the T2 is isointense.
- When eADC is applied, restricted diffusion is bright (the same as the DWI image) and T2 is isointense.
ADC and eADC Algorithms
READY View Diffusion Weighted Imaging generate parametric images from a Diffusion Weighted data set.
A diffusion-weighted MR data set contains, for each scan location, an optional reference T2* image (b=0) and one or more images representing the geometrical average of acquisitions with gradients applied along three perpendicular axes.
Typically, such a diffusion-weighted exam is composed (for each scan location) of one averaged diffusion-weighted image for a gradient strength of b=1000 sec/mm2, followed by the reference T2* image (b=0) and three acquisition images. However, the algorithm allows for data sets organized differently, or using a different gradient strength, or containing images for more than one gradient strength.
The algorithm computes the average Apparent Diffusion Coefficient (ADC) by fitting the logarithms of the pixel values I to a linear function using regression analysis, according to the equation
I(b) = I(0)*exp(–ADC*b)
or
ln (I(b) / I(0)) = –ADC*b
This regression analysis returns the value for the slope of the function, which is the desired ADC value.
The algorithm also returns a value for the exponential ADC (eADC), defined as:
eADC = exp(–ADC*b)
For data sets with only two b-values (0 and 1000 sec/mm2), this reduces to:
eADC = I(b) / I(0)
i.e., the signal attenuation (ratio of pixel values at b=1000 and b=0).
The linear regression analysis also returns a value equivalent to the standard error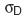 from which a confidence level can be calculated (as described above for the Correlation Coefficient algorithm).
from which a confidence level can be calculated (as described above for the Correlation Coefficient algorithm).
The confidence level has small values corresponding to high confidence and large values corresponding to low confidence. For example, a confidence level of 0.001 indicates a 0.1% probability that the logarithms of the pixel values are not proportional to the b-values.
A user-defined confidence level is used to threshold the diffusion coefficient calculation such that:
- Thresholded ADC = ADC if confidence level is <= user-defined confidence level
- Thresholded ADC = 0 if confidence level is > user-defined confidence level
The pixel locations for which the algorithm returns 0 are displayed in black on the functional map.
For data sets with only two b-values (0 and 1000 sec/mm2), the confidence level is of no use: it is always possible to obtain a perfect fit of a linear function between two points. However, for data sets with more than two b-values, it will be possible to use the confidence level parameter to eliminate noise areas. It is suggested to use a confidence level of 25% (0.25) when there are more than two b-values.
Image sequence: the algorithm automatically uses the acquired b–values in the exam.
Confidence level: by default, a confidence level of 0.1% (0.001) is used, but this value can be changed by the user (”advanced settings” in the protocol).
Unit to display maps: by default, the numerical values shown on the ADC functional map represent mm2/sec, but the user can change this to m2/sec if required (”advanced settings” in the protocol).
DWI measurement units
The DWI functional maps have the following units of measurement.
| Maps | Units |
|---|---|
| ADC | mm2/s |
| ADC | m2/s |
| eADC | None |
| ADC 10^-6 | mm2/s |
READY View protocols that use DWI scan data
- ADC
- MR Brain
- MR Breast
- MR Liver
- MR Pelvis
