- 00000018WIA30D13970GYZ
- id_400222851.6
- Aug 19, 2022 2:32:19 PM
Diffusion Tensor EPI
DW EPI Tensor or DTI is a technique that produces image contrast proportional to the local diffusion coefficient of water. Both the diffusion coefficient and its directional dependence can be measured using DTI. Data can then be used to image the directional dependence of the local diffusion coefficient in the tissue.
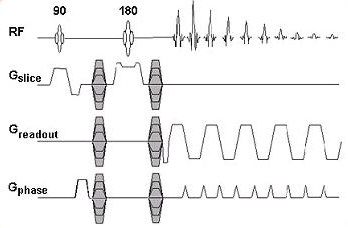
DTI pulse sequence consists of a 90° excitation pulse and a 180° RF. It also includes a pair of DW gradients, one placed before the 180° RF, the other immediately after. This pair of gradients is applied not only for the slice gradient axes, but the readout and the phase gradient axes as well.
Use DTI for brain applications. It is most commonly used for white matter tract visualizations. Visualizing the white matter tracts in the brain can be useful in monitoring patients with stroke, epilepsy, various brain trauma, neonatal brain development, as well as disease management. Up to 50,000 images can be acquired within a single DTI series.
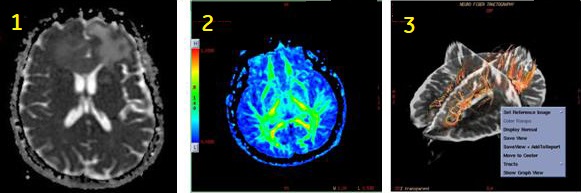
| Number | Description |
|---|---|
| 1 | DTI ADC map |
| 2 | DTI Fractional Anisotropic map |
| 3 | Fibertrak image generated in READY View |
Consider this information when modifying the Diffusion Tensor scan parameters. For specific scan parameter values, select a protocol from your GE or Site library.
- Scan selections: 2D Mode, Echo Planar Imaging family, DW EPI pulse and Diffusion Direction on the Diffusion tab, set to Tensor.
General
- See READY View: Diffusion Tensor Imaging workflow for details on the order in which functional maps are generated.
- Inform the patient prior to the scan that the there is a table vibration during a DTI acquisition. This can reduce patient motion from being startled at the beginning of the acquisition.
Scan parameters
- Bandwidth: As the RBw increases, SNR decreases, chemical shift artifact decreases, minimum TE decreases (which means the echo space decreases). As echo space decreases, geometric distortion decreases.
- Frequency/Phase: In DTI, the frequency and phase matrices default to 128, although you can choose a minimum of 64 or a maximum of 256 for both matrices. Scanning with a 128×128 matrix provides adequate resolution in a reasonable amount of scan time.
- Spacing: Do not select Interleave for spacing because images may be lost and tensor maps will not be processed. The system acquires the first phase at each location (pass 1) and then goes back and acquires the second phase at each location (pass 2) and so on. Select 0 for spacing if contiguous slices are desired.
- TR: Increasing the TR increases the amount of available slices. You should select a TR long enough to cover your imaging area within one acquisition.
- Consider selecting Real Time Field Adjustment. For details, see Real Time Field Adjustment.
User CVs
Post-process tasks
There are multiple compatible post-process tasks. For details, see Add post-process task.
- Diffusion Tensor Imaging Basic and Advanced images and maps. For details, see Diffusion Tensor Imaging considerations.
- Threshold adjustment. For details, see Threshold adjustment procedure.
- Anisotropic weight and Kernel size. For details, see DTI Optional procedure.
