- 00000018WIA3044A970GYZ
- id_400258271.3
- May 23, 2022 4:13:30 AM
Getting Started
The Volume Viewer is a powerful 3D analysis software that enables fast Volumetric Review of MR and PET data sets. It creates a 3D volume of slice data that may be displayed as Volume Rendered (VR), Surface Rendered (SR), Maximum Intensity (MIP), or Minimum Intensity (MIN).In MR, the MR General Reviewer term is interchangeable with the MR General Review.
For more information about the Volume Viewer, see Access additional operator manual instructions procedure and select the following:
- Modality: Advantage Windows
- Products: AW Volume Viewer
- Documentation Type: User and Operator Manual
- Language: English (in this example)
- Revision: Current Revision
To get familiar with the MR General Review application, read these topics:
- Open MR General Review (Volume Viewer)
- Volume Viewer workflow
- Review Controller
- Right-click menu
- Keyboard shortcuts
3D intensity based projections
A MIP (Maximum Intensity Projection) or MIN (Minimum Intensity Projection) projection traces a ray or angle through a stack of 2D images. The highest pixel intensity along the ray is displayed in the resulting image for a MIP projection. A MIN projection displays the lowest pixel intensity.
- MIP: The pixel value is the maximum voxel value along the line perpendicular to the screen. MIP is very valuable for 3D visualization of high voxel value structures (typically vessels).
Figure 1. MIP 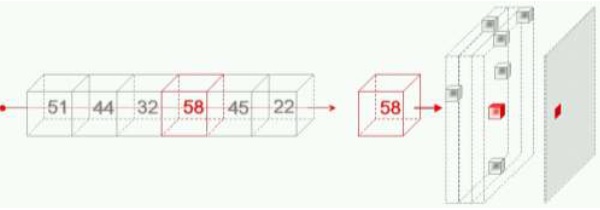
- HD MIP (High Definition Maximum Intensity Projection): this mode is identical to the “MIP” mode described above, except that image definition is greater and system processing speed is slower.
- MinIP (Minimum Intensity Projection): The pixel value is the minimum voxel value along the line perpendicular to the screen.
Figure 2. MiniIP 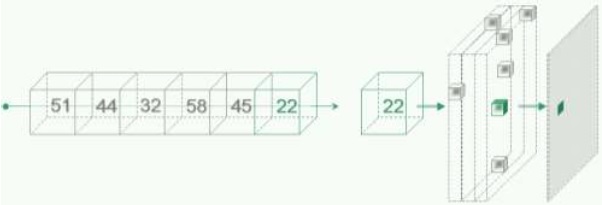
- Weighted MIP: a rendering mode providing visual information on the depth of the objects in the image. Right click the on–view annotations and select (Weighted MIP) to change the current view to a Weighted MIP view.
- RaySum: the pixel value is the sum of the voxel values along the line perpendicular to the screen. The result is similar in aspect to conventional radiography images.
- Integral: the pixel value is the sum of voxel values along a shallow depth below the displayed surface point. This mode differs from surface shading in two respects: it can show features located just below the surface of the 3D model, but it does not use shading based on the angle of the ”reflected” light so the result may look ”flatter”.
Volume Rendering (VR)
Volume Rendering is a technique that uses the concept of Opacity. For different density levels, each voxel transmits a certain amount of light, which is reflected on the following voxel, and only the residual light reaches the following layer. The resulting image is the total sum of the reflection from each layer of tissue through which the light has passed. The effect of using Volume Rendering on a dataset is that it makes highly opaque objects more visible and at the same time it makes less opaque objects more transparent.
Structures presenting density value associated with low opacity transmit light: they are translucent ![]() .
.
Structures presenting density value associated with high opacity reflect light: they are visible ![]() .
.
Surface Rendering
Surface Rendering is similar to Volume Rendering except that it first separates the volume of Interest (VOI) from the original data set and then it creates the rendered image.
