- 00000018WIA30358970GYZ
- id_400225591.5
- Mar 28, 2022 2:38:56 PM
Diffusion Tensor
READY View has two protocols to process Diffusion Tensor images to generate the parametric maps.
- DTI protocol
- DTI-Advanced protocol
The DTI protocol generates:
- Average DC
- Anisotropy Index
- Fractional Anisotropy (FA)
- Isotropic
- Volume Ratio Anisotropy
- Exponential Attenuation
- T2-weighted Trace
The DTI-Advanced protocol generates:
- Dxx Diffusion Coefficient
- Dxy Diffusion Coefficient
- Dxz Diffusion Coefficient
- Dyy Diffusion Coefficient
- Dyz Diffusion Coefficient
- Dzz Diffusion Coefficient
- Magnitude DC
- Maximum Eigen value
- Middle Eigen value
- Minimum Eigen value
- Relative Anisotropy
- Surgace DC
- Surface/Average Anisotropy
- Volume DC
- Volume/Average Anisotropy
- Volume/Surface Anisotropy
Algorithms
In an anisotropic environment, the diffusion coefficient [D] that characterizes molecule mobility can be different along each direction of space. It can be modeled by a second rank tensor, represented by a 3x3 symmetric, positive and real matrix:
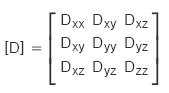
A diffusion-tensor data set contains, for each location, one or more reference T2* image(s) (b=0) and a number of acquisition images (from a minimum of 6 up to 300 images) each representing a different gradient orientation.
The Diffusion Tensor algorithm computes, for each pixel location, the six coefficients of the diffusion tensor from the data in the acquisition images.
The results are represented in the form of functional maps for isotropic image (or T2–weighted trace), average diffusion coefficient, exponential attenuation, fractional anisotropy, and volume ratio anisotropy.
| Algorithm | Description |
|---|---|
| Coefficient functions |
|
| Eigen value functions |
Mathematically, the eigen value is the factor by which a linear transformation multiplies one of its eigenvectors. In an appropriate spatial reference frame, the diffusion tensor is diagonal (contains only three nonzero elements). These elements in diffusion tensor imaging are called the eigenvalues. The vectors characterizing the reference frame are the eigenvectors.
|
| Invariant functions |
|
| Diffusion functions |
Diffusion measures the process of movement of a water molecule from an area of high concentration to an area of lower concentration. The functions defined under this category are :
|
| Anisotropy functions | Anisotropy is the property of having different values when measured in different directions. The functions plugged under this category are:
|
| Attenuation functions |
Attenuation functions measure the property of weakening density of water molecules. The functions plugged in READY View under this category is:
|
| Isotropic image functions |
for each orientation Isotropic_value = isotropic_value * pow ( T2_Signal * DW_Signal , 1.0 / ( double )_nOrientation ) Each pixel having a MR signal value lower than the threshold, without any diffusion gradient, is not processed. |
| T2W trace Functions |
|
DTI measurement units
The DTI functional maps have the following units of measurement.
| Maps | Units |
|---|---|
| DTI-Average Diffusion Coefficient | m2/s |
| DTI-Isotropic Image | None |
| DTI-Fractional Anisotropy | None |
| DTI-Volume Ratio Anisotropy | None |
| DTI-Exponential Attenuation | None |
| DTI-T2 Weighted Trace | None |
| DTI-Colored Orientation | None |
| DTI-Anisotropy Index | None |
| Dxx Diffusion Coefficient | m2/s |
| Dxy Diffusion Coefficient | m2/s |
| Dxz Diffusion Coefficient | m2/s |
| Dyy Diffusion Coefficient | m2/s |
| Dyz Diffusion Coefficient | m2/s |
| Dzz Diffusion Coefficient | m2/s |
| Magnitude DC | m2/s |
| Maximum Eigen value | m2/s |
| Middle Eigen value | m2/s |
| Minimum Eigen value | m2/s |
| Relative Anisotropy | None |
| Surface DC | m2/s |
| Surface/Average Anisotropy | None |
| Volume DC | m2/s |
| Volume/Average Anisotropy | None |
| Volume/Surface Anisotropy | None |
READY View protocols that use DTI scan data
- DTI
- DTI-Advanced
- MR Brain
