- 00000018WIA30820870GYZ
- id_400259761.5
- Jan 26, 2022 8:57:21 PM
Spatial gradient
About this task
The spatial gradient is defined as how the B0 field changes with location: if the strength of the B0 field changes by 500 G between two locations 1 cm apart, the spatial gradient is 500 G/cm between those two points.
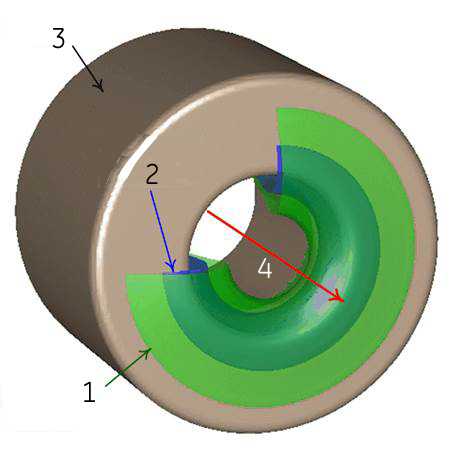
The shape of the SG field is quite different from the shape of B0. Like the B0 field, the spatial gradient’s shape is a symmetrical, three dimensional field that follows the cylindrical shape of the magnet. Figure 1 shows two spatial gradient isocontours. The green surface is at 400 G/cm. The blue is a higher spatial gradient at 700 G/cm. (The spatial gradient is the same at the front and back of the magnet – the back isocontours are removed for clarity in this figure.)
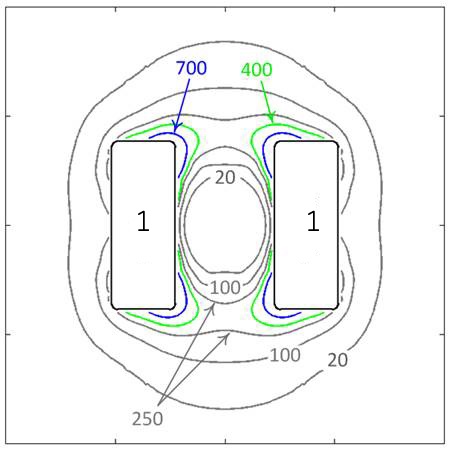
Figure 2 is a spatial gradient contour map (again, a two dimensional slice through the three dimensional field) shows the 700 and 400 G/cm contours. The contours are symmetrical around the centerline of the magnet, both side-to-side and end-to-end. Contours at 20, 100, and 250 are added, and they show three important behaviors of the spatial gradient field: